Explain the Different Types of Body Symmetry in Animals
Asymmetry is a unique feature of Parazoa Figure PageIndex2. During the embryonic larval and adult stage all organism share a similar body plan.
16 biology flashcards containing study terms like Give an example of an animal with bilateral symmetry not mentioned in the text Use the characteristics of animals to show that a Holstein cow Bos primi-genius used for milk production on dairy farms is an animal Rotifers.
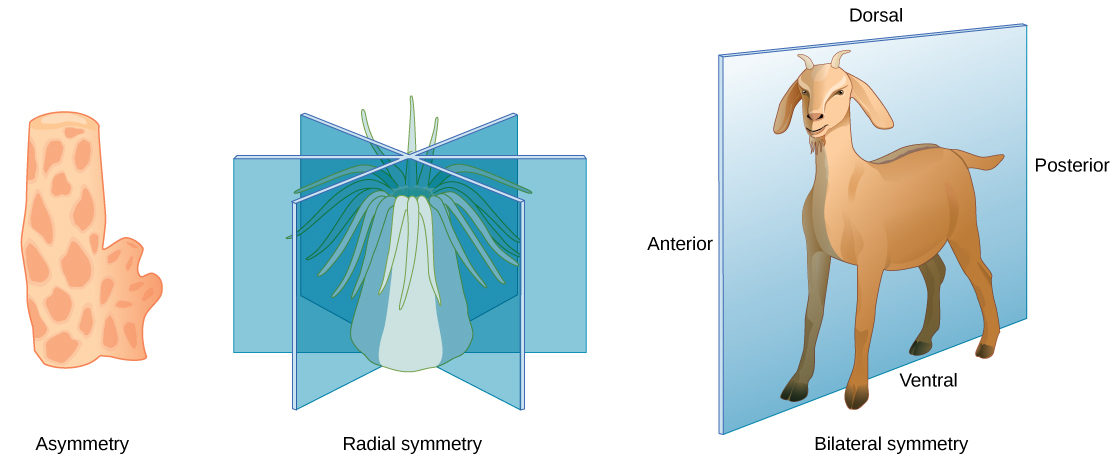
. Radial means body parts are arranged in a circle around a center point and jellyfish are an example. In bilateral symmetry a single imaginary plane divides the body into left and right sides which are similar. It is found in organisms with bilateral symmetry.
Ventral and right and left sides All true animals except those with radial symmetry. With the exception of radial symmetry external form has little relation to internal anatomy since. Also the mode of locomotion varies from one animal to another.
Animal Characterization Based on Body Symmetry. Ventral and right and left sides Figure 4. Unlike coelomates eucoelomates animals with a true body cavity acoelomates lack a fluid-filled cavity between the body wall and digestive tract.
Bilateral means two sides The animal can be divided into right and left halves and crayfish are an example. How do they differ from each other and what advantages andor disadvantages does each body cavity possess. Bilateral symmetry means that if you cut that organism from the middle you will get two equal halves.
Radial symmetry and bilateral symmetry are two different types of biological symmetries found in organisms. Animals with bilateral symmetry have a head and tail anterior vs. Examples are Coelenterates ctenophores and echinoderms.
Identify the 3 types of BODY CAVITIES that are seen in animals. The balanced distribution of the body shapes is referred to as the biological symmetry. Symmetry in biology the repetition of the parts in an animal or plant in an orderly fashion.
Locomotion in Animals and Their Body Structure. Different types of bones and muscles take part in the locomotory action. The types of symmetry are asymmetry radial symmetry bilateral symmetry and biradial symmetry.
What are the different types of body cavities. Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. Introduction and Literature Review.
Bilateral Symmetry In Animals. Specifically symmetry refers to a correspondence of body parts in size shape and relative position on opposite sides of a dividing line or distributed around a central point or axis. Learn about body plans the types of body symmetry body cavities and tissues and.
Most animals with bilateral symmetry have coeloms the human coelom is the pericardial sac around the heart. Asymmetrical radial and bilateral. Biology 21062019 2040 monk68.
All types of symmetry are well suited to meet the unique demands of a particular animals lifestyle. The body is obviously made of layers upon layers of cells and these cells are. Body cavity also acts as shock absorber and protects the internal organs.
The skeletal system in the human body helps in its locomotion. In the case of birds and animals their body structure is different from that of humans. Posterior front and back dorsal vs.
An account of the different type of symmetry in animals. The three types of symmetry are. A coelom is a body cavity.
Generally animals show two types of symmetry-Radial symmetry. How do they differ from each other and what advantages andor disadvantages does each symmetry possess. Posterior front and back dorsal vs.
Radial symmetry is the arrangement of body parts around a central axis like rays on a sun or pieces in a pie. A symmetry where any plane passing through the central axis divides the body into two equal halves is called the radial symmetry. At a very basic level of classification true animals can be largely divided into three groups based on the type of symmetry of their body plan.
Identify the different types of BODY SYMMETRIES seen in animals. Animals have different types of body symmetry. Radially symmetrical bilaterally symmetrical and asymmetrical.
Symmetry is another basis of classification of animals. The body plans of animals have different classifications and features that are affected by various factors. Biological symmetry can be divided into several categories such as radial symmetry spherical symmetry bilateral symmetry biradial symmetry and the.
Asymmetrical means it has no symmetry and sponges are an example. Explain how body symmetry is related to the phylogeny of animals. Start studying the ch.
Other questions on the subject. Only a few animal groups display radial symmetry while asymmetry is a unique feature of phyla Porifera sponges. Bilateral symmetry involves the division of the animal through a midsagittal plane resulting in two superficially mirror images right and left halves such as those of a butterfly Figure 3 crab or human body.
Body plans are the group of developmental and structural characteristics used in the identification of groups of animal mainly such as Phylum. Coelom is the main body cavity in most of the animals which is located between the intestinal canal and the body. Evolution of body cavity is an important event which further helped the formation of efficient body systems to support growing organs and distribute material.
Bilateral symmetry involves the division of the animal through a sagittal plane resulting in two mirror image right and left halves such as those of a butterfly d crab or human bodyAnimals with bilateral symmetry have a head and tail anterior vs. As these plans are used to define taxonomic groups.


Comments
Post a Comment